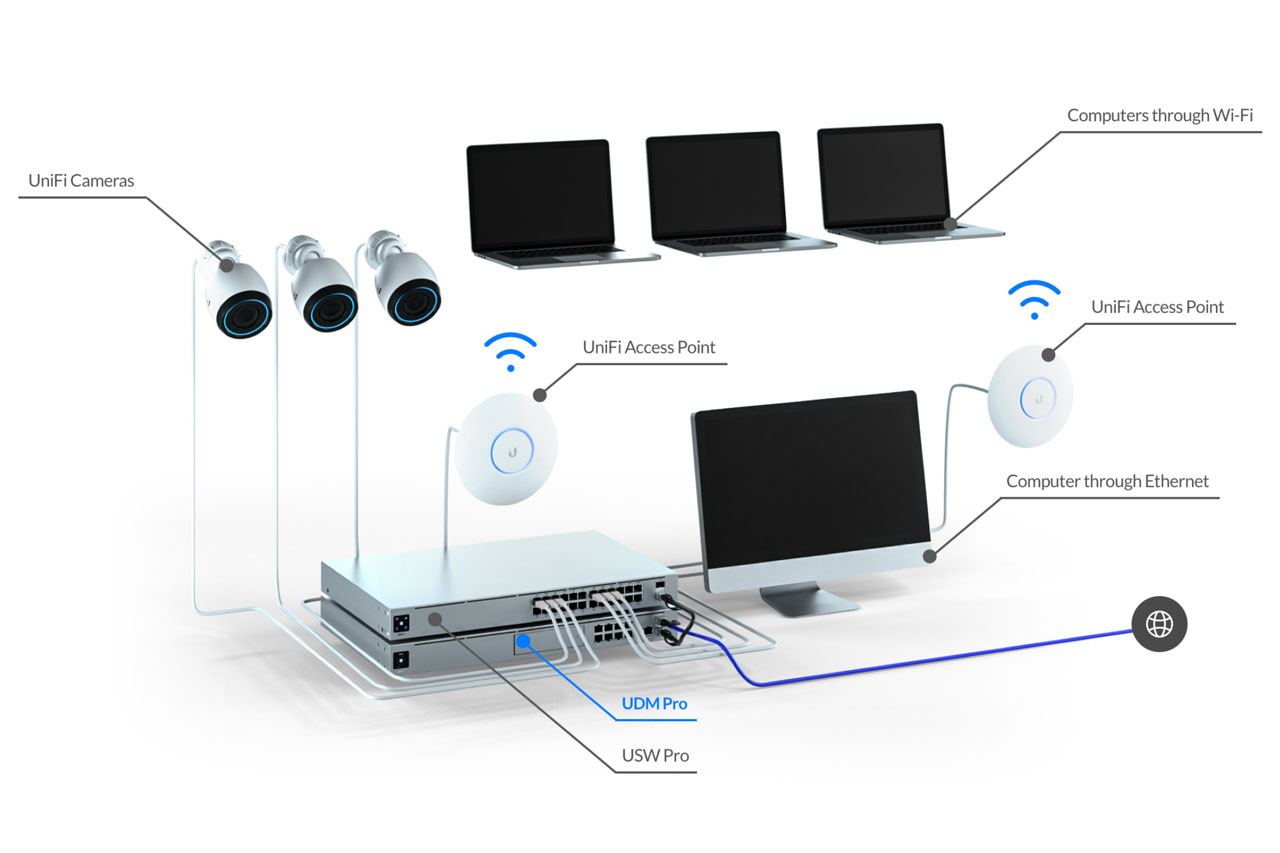
Reliable internet is one of the most important amenities at a short-term rental—and one of the most common sources of guest complaints when it isn’t configured correctly. Beyond speed, hosts need stability, security, guest isolation, and protection for smart-home devices.
For these reasons, UniFi is one of the best networking platforms available for Airbnb and vacation rentals. When configured properly, UniFi provides enterprise-grade reliability while remaining fully manageable remotely.
This guide walks through how to design, configure, and secure a UniFi network specifically for short-term rentals, with a focus on uptime, guest experience, and smart-device safety.
Why UniFi Is Ideal for Short-Term Rentals
Unlike consumer routers, UniFi is designed for environments with:
- Many transient devices
- Frequent guest turnover
- Smart locks, thermostats, sensors, and hubs
- Remote management requirements
Key advantages of UniFi for short-term rentals include:
- Centralized cloud management
- Excellent Wi-Fi performance with ceiling-mounted access points
- True guest network isolation
- VLAN support for smart devices
- Strong firewall and traffic controls
- Long-term reliability without routine reboots
For hosts who want their rental to “just work” without constant troubleshooting, UniFi is a long-term solution.
Step 1: Choose the Right UniFi Hardware
Before configuration begins, it’s important to select hardware appropriate for your property size and layout.
Core Components
Most short-term rentals will use:
- A UniFi gateway/router (e.g., Dream Router or UDM Pro)
- One or more UniFi access points
- Optional UniFi switches for expansion
Access Point Placement
For best results:
- Mount access points on ceilings or high on walls
- Avoid placing Wi-Fi equipment where guests can access or unplug it
- Use multiple access points for larger homes instead of a single powerful router
This approach improves coverage while preventing guest tampering.
Once you have configured the system, your Network Topology should look something like this:
Step 2: Protect and Secure Your Network Hardware
Guests will interact with anything they can reach. For reliability:
- Keep routers, switches, and modems in a locked closet or utility room
- Run Ethernet to ceiling-mounted access points
- Avoid placing routers in living spaces
UniFi access points are designed to be exposed; the rest of the equipment should not be.
Step 3: Configure Your Internet Modem for Reliability
Most ISP-provided devices combine a modem, router, and Wi-Fi into one unit. These devices are not designed for short-term rentals and often become unstable over time.
Best Practice
Configure your ISP device in pass-through or bridge mode, so it:
- Acts only as a modem
- Hands off routing and Wi-Fi to UniFi
- Reduces crashes and required reboots
If true bridge mode isn’t available:
- Disable Wi-Fi on the ISP device
- Disable unnecessary features
- Let UniFi handle all routing and wireless traffic
This dramatically improves stability.
Step 4: Configure WAN (Internet) Settings in UniFi
Once your UniFi gateway is connected:
- Log into unifi.ui.com
- Open the Network application
- Navigate to Internet / WAN
- Configure WAN settings using your ISP’s requirements (DHCP, PPPoE, etc.)
Step 4: Configure WAN (Internet) Settings in UniFi
1. Login to unifi.ui.com and open the Network app for the location you’re choosing to setup.
2. On the Network Dashboard, enter settings (bottom-right).
3. Click on the “Internet” tab.
4. Click on WAN1 configuration, and set it up using the configuration provided by your ISP.
- Under the Advanced section, select “Manual” and choose the appropriate IPv4 Configuration and/or IPv6 configuration.
- Typically, this will be IPv4 PPPoE, and will include credentials that you need to login to your ISP. Follow instructions provided by your ISP for proper configuration of this WAN setup.
Advanced Tip (UDM Pro Users)
If your hardware supports it, configure:
- One WAN profile for your ISP
- A secondary DHCP WAN profile
This allows fast recovery if the modem ever needs to be factory reset.
To allow for fast recovery if the modem ever needs to be factory reset, the UDM Pro allows you to setup and configure multiple WAN setups, which you can assign to different internet ports. We suggest that you configure a standard WAN setup for DHCP, which is the default of all internet devices to hand out IP addresses out of the box or factory reset, and a second WAN setup to interface with your ISP in pass-thru mode. Then, if you need to factory reset your internet access device, you simply change the port it plugs into your UDM Pro, and your UDM Pro will immediately communicate with it properly.
To do this:
- There will be an existing Primary (WAN1) configuration present that you setup above. Rename it to “Primary (ISP)” or some similar name.
- There will be a second unconfigured Secondary (WAN2) configuration, edit it and rename it to something called “Secondary (DHCP).” In the future, if things go awry, you can factory reset your internet device and switch the ports your UDM Pro is connecting with to the WAN2 port to quickly get back online and into into the internet device’s configuration.
- Leave this configuration set to “Auto” which defaults to DHCP:

- Leave this configuration set to “Auto” which defaults to DHCP:
Now that you have both WAN setups, you can easily switch between them by switching which port you connect the UniFi router to your modem. In a factory reset situation, you connect the modem to your “Default DHCP” configured port (WAN2), but once set to pass-thru, you switch the cable to the “ISP” configured port (WAN1).
Step 5: Create Your Primary (Owner & Infrastructure) Network
Your primary network should be used for:
- UniFi hardware
- Infrastructure devices
- Owner access
Recommended Settings
- Strong WPA2/WPA3 encryption
- Non-default IP range (e.g., 192.168.50.0/24)
- No guest access
This reduces conflicts and improves security.
We recommend changing the default network IP range so that there is no possibility it will conflict with your current or a future internet device’s network.
To do so, update the “Host Address” field to “192.168.50.1“. When you change this field, the Gateway, Broadcast and IP Ranges will automatically update to the new network subnet, and will look like the following:
If you’re interested content filtering on your default network or a separate “Kids” network, set the content filtering to “Family:”
Step 6: Create a Dedicated Guest Network
Guests should never share the same network as your smart devices.
Guest Network Goals
- Isolate guest devices
- Prevent access to local resources
- Allow bandwidth control
- Optional captive portal
How to Configure
- Create a new virtual network (VLAN)
- Mark it as a Guest Network
- Assign a different subnet (e.g., 192.168.199.0/24)
- Create a corresponding Wi-Fi SSID for guests
This ensures guests can only access the internet—not your devices.
From “Networks,” click “New Virtual Network,” name it “Guest”, and set a different subnet. We recommend using a very high subnet, like “192.168.199.0” and then click “Manual” under “Advanced.”
Then under “Advanced” set a large VLAN ID, like 100 as shown below, and check the “Guest Network” box, similar to the following:
When you’re done, you should have several networks with different VLAN IDs and different Subnets, similar to the following:
Setup your multiple WiFi networks for your personal devices, your guest’s devices, and any other uses you see fit.
- Click on the WiFi tab
- Add a second WiFi network which will be your guest network.
- Name it something related to your property and easy for guests to identify
- Set the WiFi password, but utilize a different password, one that is easy for your guests to remember and completely different than your
default. - Under “Network,” switch the option to “Guest” (which we just created above)
If you want to implement bandwidth controls for the guest network:
- Return to the Wi-Fi config
- Select the “Guest” Wi-Fi
- Under “Advanced” enable the “WiFi Speed Limit” and then click “Create New Profile” to create the “Guest” profile
- Set the name: Guest
- Set any download bandwidth limit if you desire
- Most importantly, if your network can be overwhelmed by too much upload, set the upload bandwidth limit
Step 7: Optional Captive Portal & Terms of Use
If desired, you can enable a captive portal to:
- Display terms of service
- Present house rules
- Add branding
This is optional, but useful in higher-traffic or premium properties.
If you want the captive portal to have guests agree to your terms of service:
- Under “Advanced” switch it to “Manual”
- Under “Hotspot” choose “Captive Portal”
- Then click the “Hotspot Portal” link to open the configuration for the Captive Portal under “Hotspot” configuration:
- Upload a logo
- Upload a background
- Set the text to be used on the captive portal
Step 8: Apply Bandwidth Limits to Guest Wi-Fi
Unrestricted uploads can cripple a network—especially if guests stream or upload heavily.
Recommended:
- Set reasonable upload limits
- Allow generous download speeds
- Prevent any single guest from saturating the connection
This keeps internet usable for everyone and protects smart devices from latency issues.
If you want to implement bandwidth controls for the guest network
- Return to the Wi-Fi config
- Select the “Guest” Wi-Fi
- Under “Advanced” enable the “WiFi Speed Limit” and then click “Create New Profile” to create the “Guest” profile
- Set the name: Guest
- Set any download bandwidth limit if you desire (we recommend none)
- Most importantly, if your network can be overwhelmed by too much upload, set the upload bandwidth limit
Set the bandwidth limit dropdown to “Guest” that you just created.
If you later need to edit the speed limit, search for “WiFi Speed Limit” in the settings and edit the “Guest” speed limit settings.
Step 9: Create an Isolated Network for Smart Devices
Smart-home devices should never live on the same network as guests—or even your primary admin network.
Why This Matters
Wi-Fi smart devices:
- Can scan the local network
- May expose vulnerabilities
- Can be compromised if isolated poorly
Best Practice
- Create a third VLAN (e.g., “Isolated”)
- Assign all smart devices and hubs to it
- Block traffic between this VLAN and all others
This protects against vulnerabilities and makes sure smart devices operate properly regardless of guest behavior:
- Smart locks
- Thermostats
- Water shutoff valves
- Sensors
- Hubs and controllers
You will need to set up a new virtual network and WiFi network for the this purpose only, you won’t want to use anything we’ve already configured.
- Return to the “Networks” tab
- Click “New Virtual Network,” name it “Isolated” or something meaningful for your use (in our example, we named it “SmartThings and
Matter”) and set a different subnet. - Click “Save”
- Return to the WiFi tab
- Create a new WiFi network, name it “Isolated” or something meaningful for your use (in our example, we named it “JF Isolated”)
- Click on the “Security” tab
- Click on the “Traffic & Firewall Rules” tab on the top
- Retain the “Simple” view, and click “Create Entry”
- Name the new rule “Block traffic to/from isolated”
- Keep Action set to “Block”
- Set Source to the new “Isolated” network, in our example named “SmartThings and Matter”
- Under Destination, select “Local Network” and then select all other networks you have created, except the “Isolated” network
- Set Traffic Direction to “Both Directions”
- Schedule set to “Always”
Now that you have the isolated network and rules established, you need to move all of your smart devices to the new isolated network.
- If your smart home hub (or any other smart device) is connected via ethernet, edit the port it is connected to so it is assigned to the
“Isolated” network:- On the far left bar, click “UniFi Devices”
- Click the switch or the router device that your smart home hub is connected to
- Click the “Port Manager” button
- Select the port number your smart hub is connected to, name the port and select your “Isolated” network:
If your smart home hub is connected via WiFi, ensure you connect it to the “Isolated” WiFi network instead of one of your others. For any WiFi smart device you own, reconnect it to the “Isolated” WiFi network.
Step 10: Apply Firewall Rules for Isolation
After creating the isolated network:
- Block all traffic to and from other networks
- Allow only internet access if required
- Keep rules simple and always active
This creates a hardened environment for automation devices.
Step 11: Connect Devices to the Correct Networks
Finally:
- Guest devices → Guest Wi-Fi
- Smart devices → Isolated Wi-Fi or VLAN
- Admin devices → Primary network
For wired devices, assign switch ports to the appropriate VLANs.
Ongoing Reliability & Maintenance
UniFi hardware does not require routine reboots.
If remote power cycling is ever needed:
- Use a smart power device for the modem only
- Reboot UniFi equipment through the cloud interface
Avoid automated power cycling of UniFi gear—it can cause configuration issues.
Why This Matters for Short-Term Rentals
A properly configured UniFi network:
- Reduces guest Wi-Fi complaints
- Prevents accidental or malicious device access
- Improves smart-home reliability
- Minimizes emergency troubleshooting
- Supports automation at scale
For properties that rely on smart locks, thermostats, and water protection, networking is not optional—it’s foundational.
UniFi provides one of the most robust networking platforms available for short-term rentals—but only when configured correctly. By separating guest traffic, isolating smart devices, and prioritizing reliability, hosts can deliver a fast, secure internet experience without sacrificing control.
A strong network doesn’t just improve guest satisfaction—it enables reliable automation, reduces risk, and allows your rental to operate smoothly even when you’re not nearby.
Once your network is set up correctly, your smart devices can operate reliably without manual oversight.